Professional MERN Stack Development on Cloud for web & mobile application
In the dynamic landscape of web and mobile application development, leveraging the power of the MERN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) combined with cloud technologies has become a hallmark of modern software engineering. This comprehensive guide delves into the realm of professional MERN stack development on the cloud, exploring the synergy between these technologies and how they empower developers to craft robust, scalable, and efficient applications.
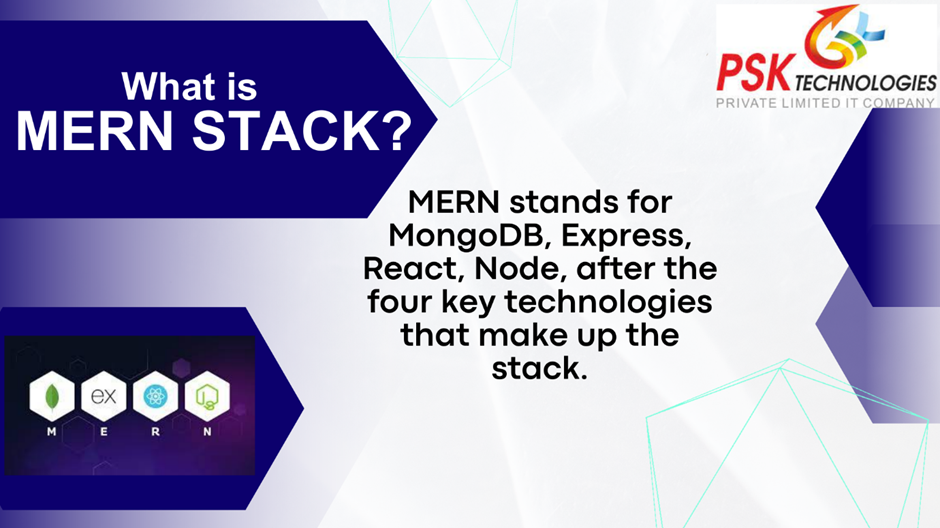
Unveiling the MERN Stack
The MERN stack encompasses a set of JavaScript-based technologies that seamlessly blend to create full-stack applications. It comprises:
MongoDB: A NoSQL database that provides flexibility in handling unstructured data and scalability for large datasets.
Express.js: A fast and minimalist backend framework for building APIs and handling HTTP requests.
React: A powerful frontend library for crafting interactive user interfaces using reusable components.
Node.js: A server-side runtime environment that allows developers to execute JavaScript code outside a web browser.
The Cloud Advantage
Incorporating cloud technologies into MERN stack development brings a multitude of benefits, ranging from scalability to security. Leading cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer a wide array of services that enhance the development process:
1. Scalability and Elasticity
Cloud platforms enable seamless horizontal and vertical scaling, allowing applications to accommodate varying levels of traffic. With auto-scaling features, resources are allocated dynamically, ensuring optimal performance without manual intervention.
2. Deployment Made Effortless
Deploying MERN stack applications on the cloud is streamlined through services such as AWS Elastic Beanstalk or Google App Engine. These platforms abstract away infrastructure management, enabling developers to focus solely on code deployment.
3. Robust Data Management
Integrating MongoDB with cloud-based databases like MongoDB Atlas ensures data durability, high availability, and automated backups. This provides developers with a solid foundation for managing critical application data.
4. Security Reinforcement
Cloud platforms offer a plethora of security features, including identity and access management, encryption, and compliance certifications. This is particularly critical when handling sensitive user data.
5. Continuous Integration and Deployment (CI/CD)
Implementing CI/CD pipelines using cloud-native tools automates the build, test, and deployment processes. This results in faster iterations, reduced manual errors, and enhanced collaboration among development teams.
6. Cost Optimization
Cloud-based solutions allow developers to pay only for the resources they consume. This cost-effectiveness is particularly advantageous for startups and businesses with fluctuating resource needs.
Crafting the Development Process
The journey of professional MERN stack development on the cloud involves several pivotal steps:
1. Environment Setup
Prepare your development environment by installing Node.js and npm. Initialize your project directories and create distinct package.json files for both the front end and back end.
2. Backend Implementation
Design your API structure and endpoints using Express.js. Connect to MongoDB using Mongoose for efficient data storage and retrieval.
3. Frontend Creation
Construct React components to form your application’s user interface. Utilize state and props for dynamic data management and incorporate third-party libraries for enhanced functionality.
4. Cloud Integration
Choose a cloud provider and set up the necessary services. Deploy your backend using serverless functions, virtual machines, or containers. Utilize cloud databases for optimal data management.
5. CI/CD and Monitoring
Implement CI/CD pipelines to automate testing, building, and deployment. Set up monitoring and logging tools to track performance and identify issues promptly.
6. Security and Optimization
Prioritize security by implementing encryption, authentication, and input validation. Optimize your application for performance by employing caching strategies and code optimization techniques.
· Embracing the Future
The fusion of the MERN stack with cloud technologies unlocks a realm of possibilities for web and mobile application development. The seamless integration of MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js with cloud platforms empowers developers to create applications that are not only feature-rich and scalable but also highly resilient and secure. By embracing this synergy, developers can navigate the ever-evolving landscape of technology and bring their innovative visions to life like never before.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KhhpUMZ5It8&list=PLgELzru4ELWgii7SgB-MNEZJjMjS_jpp1&index=6
PSK Technologies Pvt. Ltd
Web Development
Digital Marketing